1. The Hexa Faculty - To become a Stream Enterer
The Hexa Faculty
The being (All types of lives) constantly uses its six doors (called hexa faculty) opened to the outside world to identify the various things in the world. Since these six gates are engaged in roles that are unique to each other, they are referred to as faculties. These six faculties are called Hexa Faculty (Salayatana - සලායතන).
The Eye
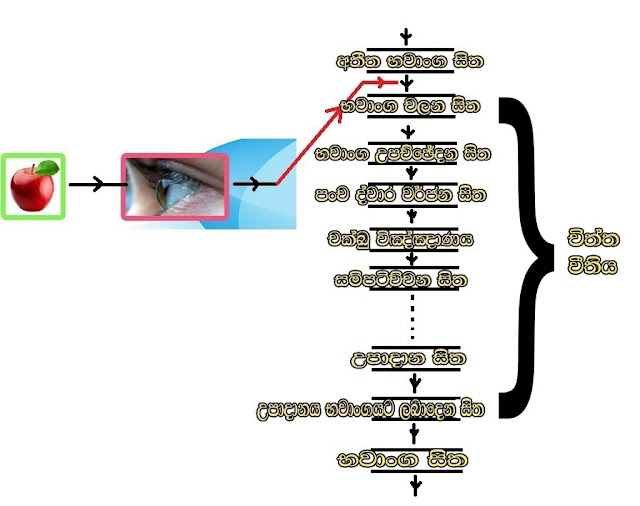
The eye is the gate through which the visible images are directed to the mind to be known by the consciousness. From this, the being's attention is directed to the image seen by the eye. Then the thought of that vision arises, that is a motive. Here the motive is a mental action (thinking) upon the vision by the intention. Due to the motive, a mind focused on the eye is born. Finally, the image seen by the eye is known by the mind.
* The mind that gives knowledge is called Consciousness. Therefore, the mind that perceives the image through the eye is called The Eye Consciousness (Chakku Vinnana - චක්ඛු විඤ්ඤාණය).
* Not an isolated single mind that starts a purpose. With that purpose, a chain of minds is born in the wilderness that is connected to each other. This chain of minds is called a Mental Pack. (Chitta Veethi - චිත්ත වීති)
* Apart from consciousness, there are minds that perform various other tasks that exist in that mental pack. But they are not called consciousness because they do not perform "objective knowing" functions.
* If the being was attentive to the image seen from the outside, it would begin to think upon that vision (Volition - සංස්කාරය - Sanskara) and the eye consciousness will be born.
* However if an image
appears to the eye when the being is unconscious or asleep with its eyes
turned away or after death, the being's attention is not directed to the eye.
Therefore Volition (Thinking with the motive) is unborn. Therefore the Eye consciousness
is also unborn. Therefore, the relevant image is not known by the being.
* In the description of Hexa Faculty, an important thing that needs to be said is that the faculty called "eye" is not the organ called the eye made up of body parts like blood, flesh, veins, etc.
The faculty eye is not
something we can see. The faculty called the eye exists as an organ within the faculty called the body. Do not treat this organ as the eye faculty (as described in Science). That organ is also
a part of the body itself.
2. The ear
* The ear is an invisible faculty like the eye. It resides in an organ within the body faculty.
3. Nose
* The mind that perceives smell through the nose is called the Nasal Consciousness (ඝාණ විඤ්ඤාණය - Ghana Vinnana)
* The nose is also invisible faculty like the eye. It resides in an organ within the body faculty.
4. Tongue
* The mind that perceives taste through the tongue is called the Tongue Consciousness (ජිව්හා විඤ්ඤාණය - Jivha Vinnana).
* The tongue is also an invisible faculty like the eye. It resides in an organ within the body faculty.
5. The Body
* The mind that is aware of touch by the body is called body consciousness (Kaaya Vinnana - කාය විඤ්ඤාණය).
* Body is not an invisible faculty like other faculties. The reason is that the body has visible images.
Based on this, the body faculty is the same "body" that we normally use that provides a habitat for the existence of the faculties such as the eye, ear, nose, and tongue.
6. The Mental Faculty
The Dhammas that come to mental faculty are:
(2) Memories
(3) Doctrines about the world
Eg: 1) It is a Dhamma that imposes a perception on an image seen by the eye-consciousness as "This is my mother".
Eg: 5) Thinking more about your friend after you got a memory about him or her is criticism. The various thoughts that arise during that criticism are Dhammas.
References
· [Abhidhamma Pitaka - Vibhangaprakaran
I - Dhatu Vibhangaya - Sections 264, 266, 268]
·
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Vibhangaprakaran
I - Institutions Vibhanga - Sections 231, 238, 241]
·
[Sutra Pitaka - Samyaka Nikaya -
Bandha Type - Ditti Samyaka - Sotapatti Type - Vata Sutra]
·
[Abhidhamma Pitaka -
Dhammasanganiprakarana - 3 Nikshepa Category - Suffering Recommendation -
Chulantara Dukha]
· [Abhidhamma Pitaka -
Kathavastuprakarana 3 - Thudusvana Type - Anantarapachaya Katha]


Thank you for this
ReplyDelete