2. The Penta Masses - To become a Stream Enterer
2.
The Penta Masses
This is quite an in-depth section. So get a
good understanding of The Hexa Faculties before studying this.
The Penta Masses are the five masses of
- Forms
- Sufferings
- Signals
- Fabrications
- Consciousness
(01) The mass of forms
Aapo – Fluid or shedding nature
Thejo - Fire or thermal nature
Vayo - Gases or wind nature
Pathavi - Solid or tough nature
- Physical things
- Non-physical things
* Penta faculties =
Hexa faculties without the mental faculty = five institutes
Non-physical things are not as above. Nerves are a type of non-physical signal that carries sensations in the body. Also, our mind is a non-physical l thing that is not captured by our five faculties. But what should not be confused here is the fact that some non-physical things can be grasped through the five faculties using some physical changes. The reason for this is that changes can be observed in physical things due to the functioning of certain non-physical things.
Ex - When one gets angry, the face may undergo some change.
That way one can observe another person's mind from the outside.
* But since the majority of non-physical functions are
unrelated with the physical things, it is difficult to confirm whether they are
true by means of the penta faculties.
Thus the physical things in the universe are taken under the
forms and the non-physical things are taken under the names (including
consciousness).
* Names = Masses of sufferings, signals, and fabrications
Accordingly, forms are all the physical things including the
four great relics as well as those born by the four great relics.
There,
The four great
relics are
Aapo, Thejo, Vayo, and Pathavi, which are taken under the
· Images visible to the eye
· Touches that sensitive to the body
Those what are
born by the four great relics are
· Sounds heard by the ear
· Odors that smell in the nose
· Flavors on the tongue
Which are born by the collisions and vibrations due to the different properties of the particles of Aapo, Thejo, Vayo, and Pathavi.
And
· Certain Dhammas felt by the mind, such as the male organ, the female organ, the life organ, etc.
Which exist by associating Aapo, Thejo, Vayo, and Pathavi.
* Life organ is the quality of having
a life of something. Accordingly, the penta masses have different life organs.
So the mass of forms is said to have life organs since the forms also have lives.
All things in the universe, i.e. the penta masses can also
be represented by 12 institutes.
They are the eye, images (sights), ear, sounds, nose, odors (smells), tongue, flavors (tastes), body, touches, mind and Dhammas.
· Images visible to the eye
· Touches that sensitive to the body
· Sounds heard by the ear
· Odors that smell in the nose
· Flavors on the tongue
Which are born by the collisions and vibrations due to the different properties of the particles of Aapo, Thejo, Vayo, and Pathavi.
· Certain Dhammas felt by the mind, such as the male organ, the female organ, the life organ, etc.
Which exist by associating Aapo, Thejo, Vayo, and Pathavi.
They are the eye, images (sights), ear, sounds, nose, odors (smells), tongue, flavors (tastes), body, touches, mind and Dhammas.
10 institutes out of those 12 institutes totally belong to the mass of forms. One institute belongs to the mass of forms to some extent. One institute does not belong entirely to the mass of forms.
* Only certain Dhammas in the Dhamma institute (ex -: life organ) belong to the mass of forms.
* The institute of Mind does not belong entirely to the mass of forms.
Forms can be presented in 6 types, considering how they are
grasped by our Hexa Faculties.
- Forms of images
- Forms of sounds
- Forms of odors
- Forms of flavors
- Forms of Touches
- Forms that belong to Dhammas
Thus, the mass of forms is the set of forms that includes
all six types of forms. Accordingly below
All the forms belonging to that 11 types (11 x 6 = 66) are
compressed into one single set and called the "mass of forms".
- Internal forms
- External forms
- Overt forms
- Subtle forms
- Insulted forms
- Honored forms
- Distant forms
- Nearby forms
- Past forms
- Current forms
- Future forms
- Internal forms are - forms that belong to someone
- External forms are - forms towards others and the outside world
- Overt forms are - eye, images, ear, sounds, nose, odors, tongue, flavors, body, and touches.
- Subtle forms are - invisible to the eye, imperceptible to the ear, and imperceptible to the nose, tongue, and body are the subtle forms belonging to the "Dhamma". Ex - female organ, male organ, empty space...etc
- Insulted forms are - images, sounds, odors, flavors, touches, etc., which are accepted as unpleasant and demeaning to people (beings).
- Honored forms are - images, sounds, odors, flavors, touches, etc., which are accepted as pleasant and respectful to people (beings).
- Distant forms are - forms that are distant from someone itself.
- Nearby forms are - forms that are close to one itself including its eye, ear, nose, tongue, and body.
- Past forms are - forms that existed at a previous moment or in a previous becoming (existence)
- Present forms are - forms that exist in the present
- Future forms are - forms to be born in the next moment or in the next becoming (existence)
( 02) The Mass of Sufferings
There is a non-physical quality called "Suffering" which is imparted to the being when the being touches physical or non-physical things in the world. Therefore, the image, sound, odors, flavors, touch, and Dhamma which are grasped by Hexa Faculties have sufferings. They are experienced by the being by touch.- Physical Sufferings (Sufferings about the physical body)
- Mental Sufferings (Sufferings about the mind)
- The suffering of the comfort
- The Suffering of the pain
- The suffering of the happiness (joy)
- The Suffering of the sadness (sorrow, fear, etc.)
- The suffering of the indifferent (moderate without both happiness and sadness)
So there are sufferings of happiness, sadness, and
indifferent in the Dhammas.
Accordingly, the sufferings can be presented in 6 types,
considering how they are grasped by our hexa faculties.
All of the sufferings belonging to that 11 types (11 x 6 = 66)
are compressed into one single set and called "mass of sufferings".
According to the Paticcha Samuppada, as anything is grasped
by Hexa faculties such as seeing an image with the eye,
- Suffering in image (Indifferent -Mental)
- Suffering in sound (Indifferent -Mental)
- Suffering in odors (Indifferent -Mental)
- Suffering in flavor (Indifferent -Mental)
- Suffering in touch (Comfort or Pain -Physical)
- Suffering in Dhammas (Happiness, sadness or indifferent -Mental)
- Internal sufferings
- External sufferings
- Overt sufferings
- Subtle sufferings
- Insulted sufferings
- Honored sufferings
- Distant sufferings
- Nearby sufferings
- Past sufferings
- Current sufferings
- Future sufferings
(0 3) The Mass of Signals
The signal is the recognition of something physical or non-physical by a being. There will be born the Contact by the flow of Patichcha
Samuppada as ignorance suffix leads to fabrication etc.
Here the eye consciousness (or relevant consciousness) makes
a judgment by joining together with the eye and image in that Contact step.
Accordingly the signal of what is the image is born. And identified.
Ex:-When you see your mother, you recognize her as "mother", but when someone else sees your mother, he/she recognizes her as "aunt" etc. That it creates different signals for different people according to the previous recognition knowledge of that image.
Ex:-When you see your mother, you recognize her as "mother", but when someone else sees your mother, he/she recognizes her as "aunt" etc. That it creates different signals for different people according to the previous recognition knowledge of that image.
Ex:-When seeing an apple (a form), one person may recognize
it as a "pleasant thing", but another person may recognize it as
"unpleasant thing".
Ex:-Due to a physical pain (a suffering), the signal of
"suffering is a pain" arises on the touch it brings.
Ex:-When you get an old sad memory (a signal), you get the
signal as "that is a bad memory for me".
Ex:-When a lustful mind is born to you (a consciousness) you
get the signal "It is a lustful mind".
Ex:-When you think (a fabrication) you get the signal of
"I have thought".
All these signals are recognitions arising from various
things that are grasped by our hexa faculties. So the signals can be presented
in 6 types.
Thus, the mass of signals is the set of signals that
includes all six types of signals. Accordingly below
All of the signals belonging to that 11 types (11 x 6 = 66)
are compressed into one single set and called "mass of signals".
The reasons related to the formation of each fabrication
should exist. Accordingly, the fabrications mean the birth by causes. In
the study about the universe, we do not find anything that is born irrationally
(causeless) in the universe. So there is fabrication in everything in the
universe.
- Signals of images
- Signals of sounds
- Signals of odors
- Signals of flavors
- Signals of touches
- Signals of Dhammas
- Internal signals
- External signals
- Overt signals
- Subtle signals
- Insulted signals
- Honored signals
- Distant signals
- Nearby signals
- Past signals
- Current signals
- Future signals
(0 4) The Mass of Fabrications
Fabrication is the generative nature of something physical or non-physical. Since these fabrications are born due to certain reasons and
so those reasons are also the fabrications born by certain reasons. Therefore,
anything that arises in this world is sustained by its causes, so along with
the extinction of those causes, the thing that is born also perishes.
Therefore "all fabrications are perishable".
Everything that is born is bound to perish.
Ex:-Lighting a lamp is the generation of the lamp flame.
Accordingly, its fabrication is the generation of that flame.
For the light of a lamp followings support as suffixes.
- The lamp
- Oil
- The lampshade
- The air
If any single cause or suffix is not available, the light of the lamp is not created. Also, the lamp also starts to be destroyed (extinguished) if even one of these causes or suffixes is used up.
- By the end of the lampshade
- Fire extinguished by wind or anything else
- By breaking the lamp
- Running out of oil
- Without getting air
Accordingly, the light of the lamp is a fabrication that arises due to the above causes and which ceases with the demise of the above causes.
- The mass of form is born by the reasons of four great relics. Therefore there are fabrications in the mass of forms.
- The masses of Pain and signal are born by the contact. Accordingly, there are fabrications in those masses as well.
- The mass of consciousness is born by names and forms. Accordingly, there are fabrications in the mass of consciousness.
- There are certain causes and suffixes for the generative nature (Fabrications) of the above four masses. That is, certain causes and suffixes must exist for the formation of fabrications too. Accordingly, the mass of fabrications is also caused by causes and suffixes. Thus there are fabrications in the mass of fabrications.
Although the fabrication mass is defined in this way, the
above-mentioned fabrications which are taken under the mass of fabrications are
also generated by certain causes and suffixes. So it is said that there are
fabrications within the fabrications. In that sense, the mass of fabrication is
also said to be fabrications. In that sense, the fabrications in the Mass of
Fabrications are also taken under the Mass of Fabrications itself.
Examples of certain fabrications as mentioned in the
Tripitaka are as follows.
Inhale, exhale, contact, Motives, Austere, Criticisms, Bliss, Sorrow,
Concentration, faith, Effort, Attention, Trance, Perception, Life, Right View,
Right Concepts, and other steps of the noble eightfold path, absence of greed, absence of the hatred, absence of the delusion,… etc.
And at the same time, the mass of sufferings, the mass of consciousness, and any of formless Dhammas which was different but occurred by
causes and suffixes are examples of the mass of the fabrications.
While studying the Paticcha Samuppada, the fabrications can
be presented as follows.
There are 6 types of motives (fabrications) according to
which motive is taken by hexa faculties.
- Merit fabrications
- Demerit fabrications
- Formless merit fabrications
- Physical fabrications
- Conceptual fabrications
- Mental fabrications
- Motives on the image
- Motives on the sound
- Motives on the smell
- Motives on the taste
- Motives on the touch
- Motives on the Dhamma
- Internal fabrications
- External fabrications
- Overt fabrications
- Subtle fabrications
- Insulted fabrications
- Honored fabrications
- Distant fabrications
- Nearby fabrications
- Past fabrications
- Current fabrications
- Future fabrications
(0 5) The Mass Consciousness
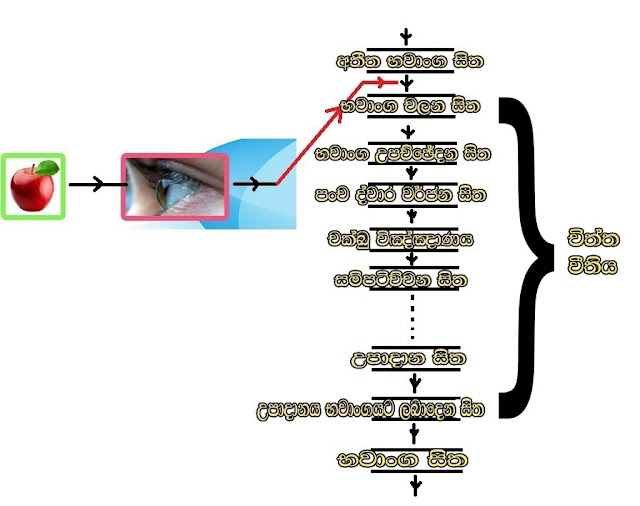
Consciousness is born by the fabrications. Knowing (getting known) physical or non-physical things in the universe by a certain being through his mind is defined as the Consciousness. First, there will be born a fabrication when the eye sees an image.
The fabrication means the occurrence of the birth of the mind (thought) of "what
was grasped by this eye". That is the motive (intention). Due to this
fabrication, a mind focused on the eye is born. This mind get known the image
seen by the eye as an image with its real form (just as an Arahat sees). The
mind what got known the image defines as the consciousness (there are many
types of minds. But all minds are not called as consciousness). This
consciousness is called “Eye Consciousness”
because it locates the eye at birth.
The eye-consciousness is not a mind tainted by defilements.
This is the luminescent mind that perceives the image seen by the eye as in reality.
Ex:-Imagine you see your mother. Then you see only a physical image through the knowledge of the eye consciousness born by the suffix of the fabrication. There will not occur a signal by identifying “this image is my mother” after analyzing the image that was seen.
Ex:-Imagine you see your mother. Then you see only a physical image through the knowledge of the eye consciousness born by the suffix of the fabrication. There will not occur a signal by identifying “this image is my mother” after analyzing the image that was seen.
* This pure mind born in this way becomes defiled by defilements at the contact step of the Patichcha Samuppada. Thus,
- Eye consciousness is born by seeing an image with the eye
- Ear consciousness is born by hearing a sound in the ear
- Nose consciousness is born by inhaling an odor with the nose
- Tongue consciousness is born by taking a taste with the tongue
- Body consciousness is born by contacting a touch with the body
- Mental consciousness is born by getting a DHamma in the mental faculty
- Internal consciousnesses
- External consciousnesses
- Overt consciousnesses
- Subtle consciousnesses
- Insulted consciousnesses
- Honored consciousnesses
- Distant consciousnesses
- Nearby consciousnesses
- Past consciousnesses
- Current consciousnesses
- Future consciousnesses
References in Tripitaka
[Sutra Pitakaya - Buddaka Nikaya -
Patisambhidamaggappakarana - Maha Kura - Ditti Katha - Atmanu Ditti]
[Sutra Pitaka - Composition Denomination - Bandha Type - Bandha Composite - Subtype - Upadana Parivatatta Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Composition Denomination - Bandha Type - Bandha Composition - Khajjaniya Type - Khajjaniya Sutra]
About the mass of forms -
[Sutra Pitaka - Buddaka Nikaya - Petakopadesha - Shasta Bhumi]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Dhammasanganiprakaran - 2 Rupa Group - Rupa Vibhatti - Suffering Recommendation]
[Abhidham Pitaka - Vibhangaprakaran 1 - Skanda Vibhangaya - Sutrataya Jaraliya - 8]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Vibhangaprakarana 2 - Dhammahadaya Vibhangaya - 1106]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Vibhangaprakarana - Paticcha Samuppada Vibhangaya - 373]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Vibhangaprakarana 1 - Institute Vibhanga - 231 - 237]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Dhatukatha Prakarana - Recommendations - 1 Collection Unsung Words Recommendation]
About the mass of sufferings -
[Sutra Pitaka - Samyutta Nikaya - Salayatana Type - Vagana Sangota - Rohagata Type - Panchakaoga Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Samyutta Nikaya - Maha Type - Indriya Samyukta - Sukhindriya Type - Tatiya Vibhanga Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Buddaka Nikaya - Petakopadesha - Shasta Bhumi]
About the mass of signals -
[Tripitaka - Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - Ekadasaka Nipataya - Nissaya Sarva - Pathama Sannya Sutra / Manasikara Sutras]
[Sutra Pitaka - Buddaka Nikaya - Petakopadesha - Shasta Bhumi]
[Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - Ekta Nipata - Ekadhamma Pali - Achurasanghata Type - 1.16.6. 73-92]
[Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - Dukha Nipata - Lower Type - 2.2.10.3]
[Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - Panchaka Nipataya - Type of Sannya - Pathama and Dutya Sannya Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - Chukka Nipataya - Maha Kura - Nibbedhika Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - Sattaka Nipata - Avyakata Type - Pachalayana Sutra]
[Tripitaka - Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - Dasaka Nipataya - Anisansa Sutra - Sariputta Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Buddaka Nikaya - Patisambhidamaggappakarana - The Great Kind - Jnanakatha - 49 Satya Vivartha Jnanaya]
[Sutra Pitakaya - Buddaka Nikaya - Patisambhidamaggappakarana - Maha Kura - Ditti Katha - Atmanu Ditti]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Vibhangaprakarana 2 - Buddhakavatthu Vibhangaya - 870 - 886]
[Abhidharma Pitakaya - Dhammasanganiprakarana - 1 Chitthothpadakandaya - Pathaman Chittang - Padabhajaniyang and Kottasavaro]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Dhatukatha Prakarana - Recommendations - 1 Collection Unsung Words Recommendation]
About the mass of fabrications -
[Sutra Pitakaya - Buddaka Nikaya - Patisambhidamaggappakarana - Maha Katha - Ditti Katha - Atmanu Ditti]
[Sutra Pitaka - Samyutta Nikaya - Salayatana Type - Chitta Samyuttha - Duthiya Kamabhu Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Buddaka Nikaya - Udana Pali - Pataligamiya Type - First Dabba Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Buddaka Nikaya - Petakopadesha - Shasta Bhumi]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Narration 2 - Eighth Type - Life Organ Stories]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Story Version 2 - Newcomer Type - Anusaya Anarammanana'ti Katha]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Kathavastuprakarana 2 - Newbie Type - Gnanam Anarammananti Katha]
[Sutra Pitaka - Buddaka Nikaya - Petakopadesha - Saptama Bhumi - 15 - 12]
[Abhidharma Pitakaya - Dhammasanganiprakarana - 1st Chitthotpada Group - Pathaman Chittang - Padabhajaniyang and Kottasavaro]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Vibhangaprakarana 1 - Skanda Vibhangaya - Sutrataya Jaraliya - 35 onwards]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Dhatukatha Prakarana - Recommendations - 1 Collection Unsung Words Recommendation]
[Sutra Pitaka - Compound Denomination - Salayatana Type - Pain Compound - Rohagata Type - Rohagata Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - One Nipata - Shuka Type - 8]
About the mass of consciousnesses -
[Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - One Nipata - Shuka Type - 9]
[Tripitaka - Sutra Pitaka - Samyutta Nikaya - Nidana Sutra - Abhisamaya Samyutya - 7 Maha Sutra - Assuthavantu Sutra]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Dhatukatha Prakarana - Recommendations - 1 Collection Unsung Words Recommendation]
[Sutra Pitaka - Composition Denomination - Bandha Type - Bandha Composite - Subtype - Upadana Parivatatta Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Composition Denomination - Bandha Type - Bandha Composition - Khajjaniya Type - Khajjaniya Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Buddaka Nikaya - Petakopadesha - Shasta Bhumi]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Dhammasanganiprakaran - 2 Rupa Group - Rupa Vibhatti - Suffering Recommendation]
[Abhidham Pitaka - Vibhangaprakaran 1 - Skanda Vibhangaya - Sutrataya Jaraliya - 8]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Vibhangaprakarana 2 - Dhammahadaya Vibhangaya - 1106]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Vibhangaprakarana - Paticcha Samuppada Vibhangaya - 373]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Vibhangaprakarana 1 - Institute Vibhanga - 231 - 237]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Dhatukatha Prakarana - Recommendations - 1 Collection Unsung Words Recommendation]
[Sutra Pitaka - Samyutta Nikaya - Salayatana Type - Vagana Sangota - Rohagata Type - Panchakaoga Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Samyutta Nikaya - Maha Type - Indriya Samyukta - Sukhindriya Type - Tatiya Vibhanga Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Buddaka Nikaya - Petakopadesha - Shasta Bhumi]
[Tripitaka - Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - Ekadasaka Nipataya - Nissaya Sarva - Pathama Sannya Sutra / Manasikara Sutras]
[Sutra Pitaka - Buddaka Nikaya - Petakopadesha - Shasta Bhumi]
[Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - Ekta Nipata - Ekadhamma Pali - Achurasanghata Type - 1.16.6. 73-92]
[Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - Dukha Nipata - Lower Type - 2.2.10.3]
[Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - Panchaka Nipataya - Type of Sannya - Pathama and Dutya Sannya Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - Chukka Nipataya - Maha Kura - Nibbedhika Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - Sattaka Nipata - Avyakata Type - Pachalayana Sutra]
[Tripitaka - Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - Dasaka Nipataya - Anisansa Sutra - Sariputta Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Buddaka Nikaya - Patisambhidamaggappakarana - The Great Kind - Jnanakatha - 49 Satya Vivartha Jnanaya]
[Sutra Pitakaya - Buddaka Nikaya - Patisambhidamaggappakarana - Maha Kura - Ditti Katha - Atmanu Ditti]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Vibhangaprakarana 2 - Buddhakavatthu Vibhangaya - 870 - 886]
[Abhidharma Pitakaya - Dhammasanganiprakarana - 1 Chitthothpadakandaya - Pathaman Chittang - Padabhajaniyang and Kottasavaro]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Dhatukatha Prakarana - Recommendations - 1 Collection Unsung Words Recommendation]
[Sutra Pitakaya - Buddaka Nikaya - Patisambhidamaggappakarana - Maha Katha - Ditti Katha - Atmanu Ditti]
[Sutra Pitaka - Samyutta Nikaya - Salayatana Type - Chitta Samyuttha - Duthiya Kamabhu Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Buddaka Nikaya - Udana Pali - Pataligamiya Type - First Dabba Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Buddaka Nikaya - Petakopadesha - Shasta Bhumi]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Narration 2 - Eighth Type - Life Organ Stories]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Story Version 2 - Newcomer Type - Anusaya Anarammanana'ti Katha]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Kathavastuprakarana 2 - Newbie Type - Gnanam Anarammananti Katha]
[Sutra Pitaka - Buddaka Nikaya - Petakopadesha - Saptama Bhumi - 15 - 12]
[Abhidharma Pitakaya - Dhammasanganiprakarana - 1st Chitthotpada Group - Pathaman Chittang - Padabhajaniyang and Kottasavaro]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Vibhangaprakarana 1 - Skanda Vibhangaya - Sutrataya Jaraliya - 35 onwards]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Dhatukatha Prakarana - Recommendations - 1 Collection Unsung Words Recommendation]
[Sutra Pitaka - Compound Denomination - Salayatana Type - Pain Compound - Rohagata Type - Rohagata Sutra]
[Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - One Nipata - Shuka Type - 8]
[Sutra Pitaka - Anguttara Nikaya - One Nipata - Shuka Type - 9]
[Tripitaka - Sutra Pitaka - Samyutta Nikaya - Nidana Sutra - Abhisamaya Samyutya - 7 Maha Sutra - Assuthavantu Sutra]
[Abhidhamma Pitaka - Dhatukatha Prakarana - Recommendations - 1 Collection Unsung Words Recommendation]







Thank you
ReplyDelete